It has been proposed that a b type lamin gene is the ancestral gene of the lamin family and that lmna may have developed from this gene by the insertion of an extra exon exon 11 during evolution 28 interestingly the insertion of exon 11 nor mally generates lamin a but mis splicing can lead to a product from a cryptic splice site within exon 11.
Berrant splicing of lamin a.
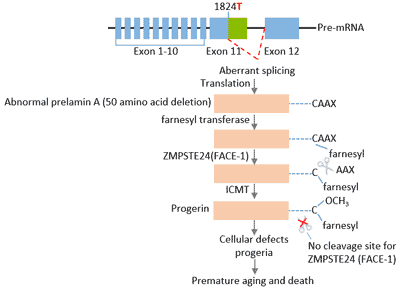
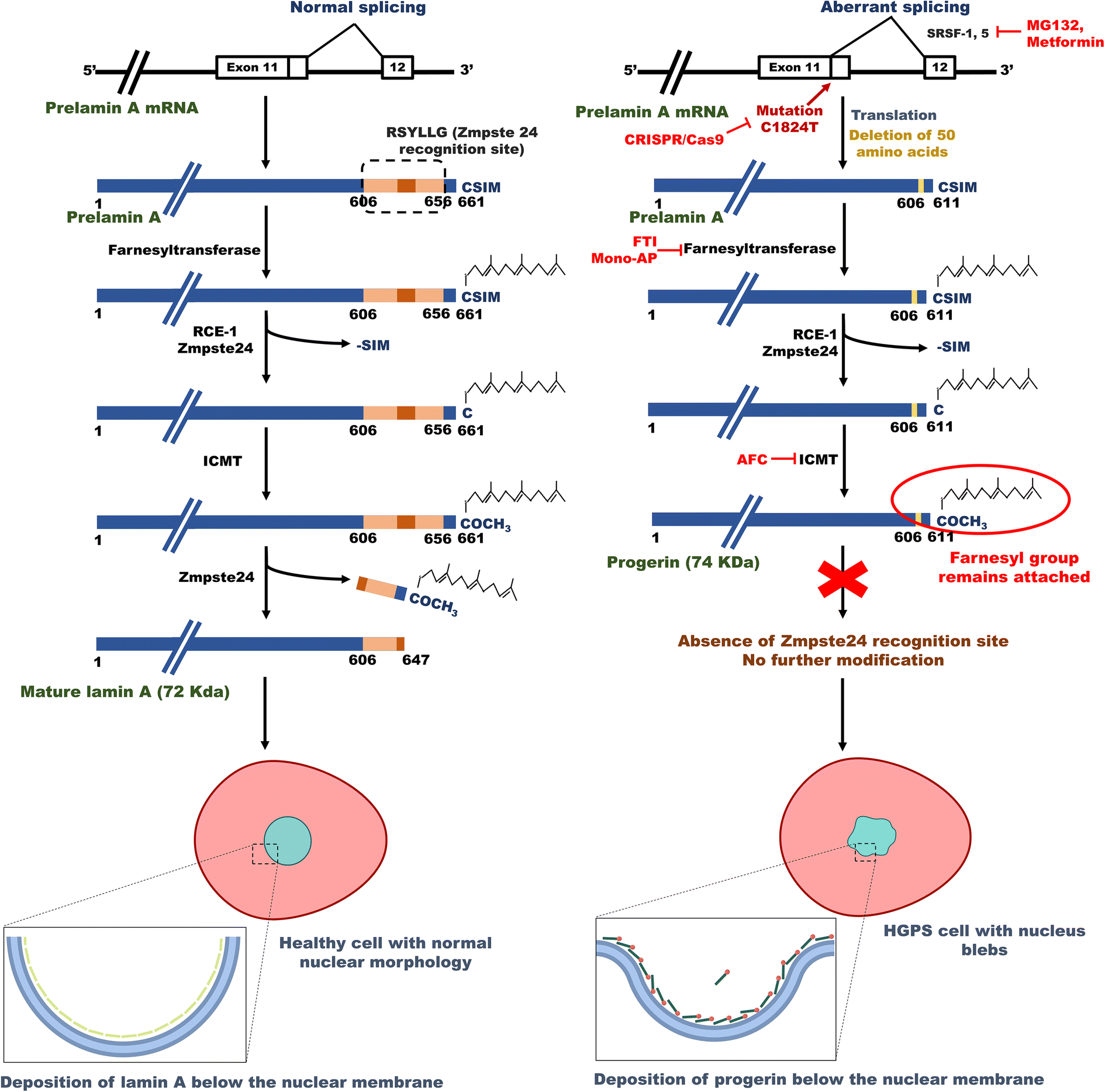
A well known example is a mutation in lmna which introduces a novel 5 splice site and generates a truncated lamin a protein that impairs nuclear membrane function.
A truncated protein of the expected molecular weight was detected in wild type cells by antibodies against lamin a and c lamin a c upon extraction of soluble proteins and enrichment for membrane associated.
Different proteins are produced by alternative splicing and or polyadenylation of the lmna gene including lamin a lamin c and progerin fig.
Due to alternative splicing the lamin a gene generates several isoforms including lamin a c c2 and lamin ad10 cau et al.
To identify small molecule modulators of aberrant lmna splicing a homogenous assay was constructed in hela cells that used a gfp containing minigene to report on correction of aberrant splicing in lamin a and a rfp dsred2 to report on cell viability uniformity and nonspecific effects on the assay signal.
The alternatively spliced products of lmna lamin c and prelamin a the precursor to lamin a are produced in similar amounts in most tissues and have largely redundant functions this redundancy suggests that diseases such as hutchinson gilford progeria syndrome hgps that are caused by prelamin a specific mutations could be treated by shifting the output of lmna more toward lamin c.
The two main isoforms lamin a and c are constitutive components of the fibrous nuclear lamina and have diverse physiological roles ranging from.
The lmna gene gives rise to at least three isoforms lamin a c lamin aδ10 as a result of normal alternative splicing regulated by cis and trans acting regulatory factors as well as the 5 and 3 untranslated regions of the gene.
Carboni n 1 floris m mateddu a porcu m marrosu g solla e cocco e mura m marini s maioli ma piras r aste r marrosu mg.
1a lamin a and lamin c are major components of the nuclear lamina a complex molecular interface located between the inner membrane of the nuclear envelope and chromatin lamins a and c are also distributed throughout the nucleoplasm.
This leads to global gene expression changes and premature aging.
The two main isoforms lamin a and c are constitutive components of the fibrous nuclear lamina and have diverse physiological roles ranging from.
The occurrence of lamin a aberrant splicing in wild type cells suggests that δ50 lamin a is present in cells from healthy individuals.
Aberrant splicing in the lmna gene caused by a novel mutation on the polypyrimidine tract of intron 5.